-
Jun 4, 2018
User Feedback
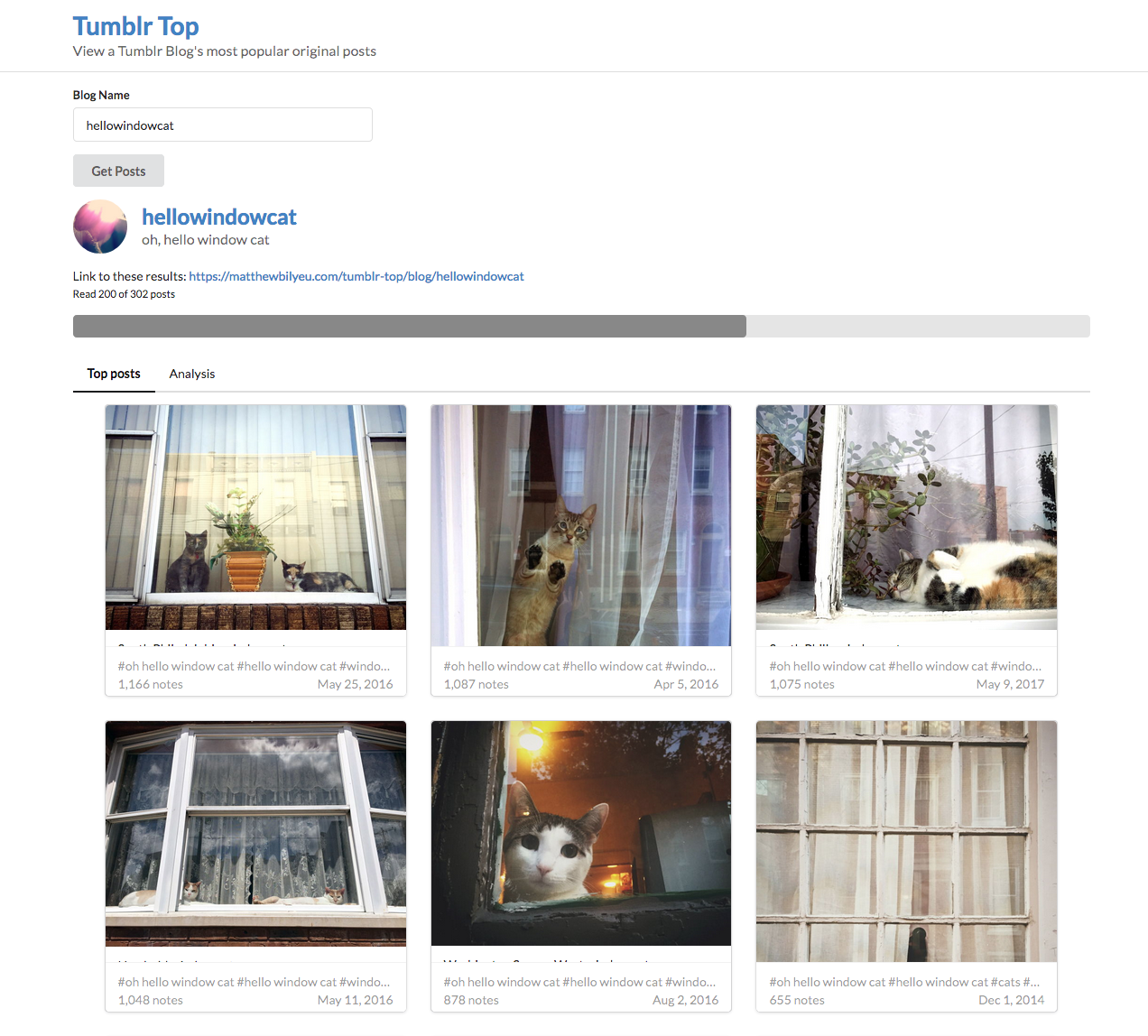
I spent some of my free time over the past three weeks rebuilding a small single page app I maintain: Tumblr Top (code here).
The original incarnation of this app was written circa 2015 in CoffeeScript and AngularJS 1.4. The new version is in React and Semantic UI. There are also a few simple charts to visualize blog post and tag popularity that were coded using the Victory charting library.
I rewrote the app as an excuse to use React on a personal project and to make the site easier to build and maintain going forward. But the original version was running smoothly with something like 2-3k users per month. I didn’t want to upset the regular users by fixing what wasn’t broken.
So I built out the updated site to what I thought was a reduced but perhaps satisfactory level of functionality. I hosted the new app at a different url, and added a callout to the old site asking users to try it out.
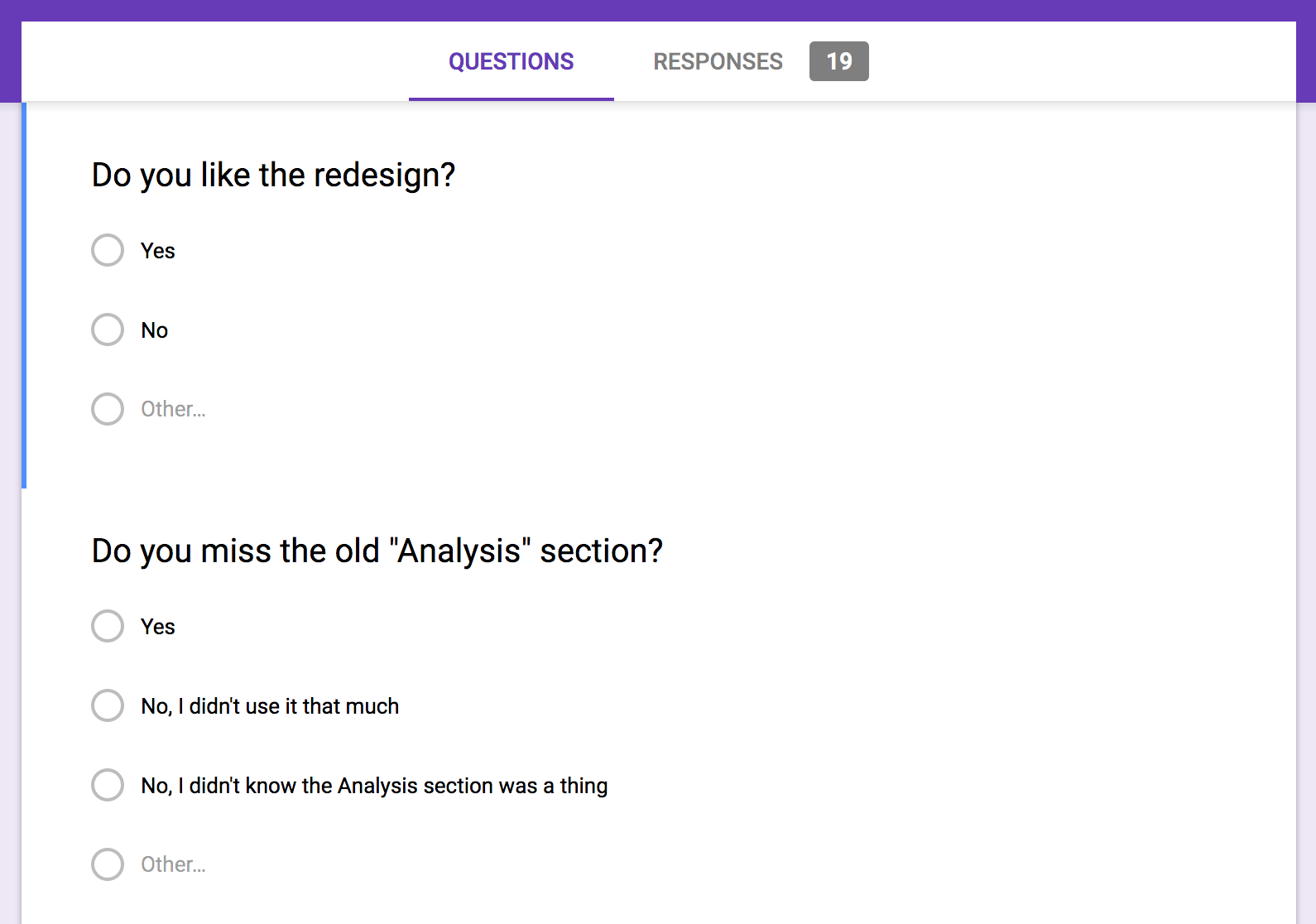
While the new app was in-progress, I invited the early adopters to leave comments and criticism. Google Forms made soliciting and collecting user feedback dead simple (alternatives: SurveyMonkey or Typeform). The feedback survey was to the point. It only had four questions:
- Do you like the redesign?
- Do you miss the [missing feature]?
- Were there any errors or bugs with the redesign? (If so, please provide your browser / operating system)
- Any other feedback about the redesign or the app in general?
Over the course of a couple weeks the survey received 19 responses. This was enough to help me massively improve the first cut. The answers to those four questions gave me a lot of insight:
- The performance improvements I’d added had come at the cost of my API access often being rate-limited
- There was a critical display bug in a browser I hadn’t tested
- Other small bugs were highlighted
- Users had become very accustomed to what I thought were unimportant design details of the original version
- A feature I thought was useless was meaningful to a large percentage of users
- Strangers on the internet are willing to fill out a survey
- You can’t please everybody
I’m thankful to the handful of power users who took time out of their lives to provide valuable feedback for the app. Without that survey I may have shipped a shoddy update and degraded my users’ experience.
-
Apr 12, 2018
Spreadsheet Jeopardy!
My girlfriend and I often watch Jeopardy! together, and we play along and keep score to make it more fun.
To avoid having to pause the show to wager, we have a house rule that “Daily Double”s are just worth twice their marked value. E.g., a D.D. on a $600 clue would be worth $1200. And we yell the answers (questions?) instead of buzzing in.
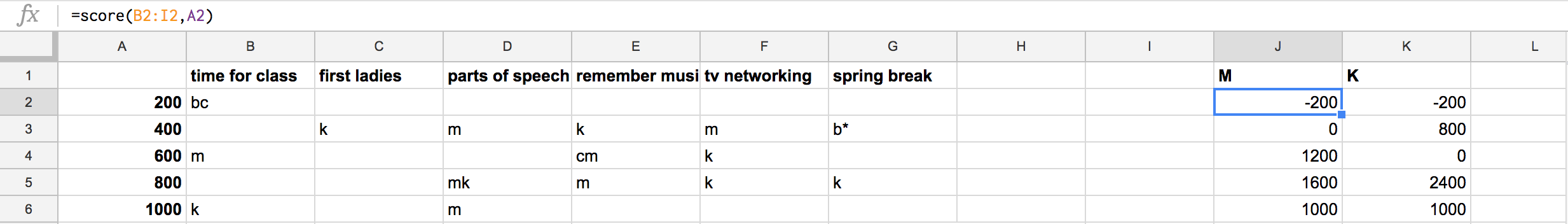
After tallying a number of games by hand, I decided to make a custom function in Google Sheets to keep score. Our scoring notation is:
- correct: first initial of first name
- incorrect: first initial of last name
- daily double: initial followed by asterisk
function score(results, level) { mScore = 0; kScore = 0; results[0].forEach( function(cell) { cell = cell.toLowerCase() if (cell.match(/.*m\*.*/)) { mScore += 2 * level; } else if (cell.match(/.*m.*/) !== null) { mScore += level; } else if (cell.match(/.*b\*.*/)) { mScore -= 2 * level; } else if (cell.match(/.*b.*/)) { mScore -= level; } if (cell.match(/.*k\*.*/)) { kScore += 2 * level; } else if (cell.match(/.*k.*/)) { kScore += level; } else if (cell.match(/.*c\*.*/)) { kScore -= 2 * level; } else if (cell.match(/.*c.*/)) { kScore -= level; } }) return [[mScore, kScore]]; }(Yes, I’m aware this could be refactored)
It just occurred to me that I could probably modify this function to gift me a stray hundred dollars every now and then. She probably wouldn’t notice… 😈
-
Apr 9, 2018
Setting Emacs Theme Based on Ambient Light
I sit next to a window at work. On sunny days it’s easier to see a light editor theme, and when the sky is dark, a dark theme is easier on my eyes. So I decided to try to have my MacBook automatically switch the Emacs theme based on readings from the ambient light sensor.
There are two parts to this solution: a command-line executable to read data from the sensor, and then a small elisp function to do the theme switching.
The program below is from StackOverflow and slightly modified. It gets the
AppleLMUControllerIO service, then, when the service is ready, prints the light sensor data to stdout and exits.// lmutracker.mm // // clang -o lmutracker lmutracker.mm -framework IOKit -framework CoreFoundation #include <mach/mach.h> #import <IOKit/IOKitLib.h> #import <CoreFoundation/CoreFoundation.h> static double updateInterval = 0.1; static io_connect_t dataPort = 0; void updateTimerCallBack(CFRunLoopTimerRef timer, void *info) { kern_return_t kr; uint32_t outputs = 2; uint64_t values[outputs]; kr = IOConnectCallMethod(dataPort, 0, nil, 0, nil, 0, values, &outputs, nil, 0); if (kr == KERN_SUCCESS) { printf("%8lld", values[0]); exit(0); } if (kr == kIOReturnBusy) { return; } mach_error("I/O Kit error:", kr); exit(kr); } int main(void) { kern_return_t kr; io_service_t serviceObject; CFRunLoopTimerRef updateTimer; serviceObject = IOServiceGetMatchingService(kIOMasterPortDefault, IOServiceMatching("AppleLMUController")); if (!serviceObject) { fprintf(stderr, "failed to find ambient light sensors\n"); exit(1); } kr = IOServiceOpen(serviceObject, mach_task_self(), 0, &dataPort); IOObjectRelease(serviceObject); if (kr != KERN_SUCCESS) { mach_error("IOServiceOpen:", kr); exit(kr); } setbuf(stdout, NULL); updateTimer = CFRunLoopTimerCreate(kCFAllocatorDefault, CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent() + updateInterval, updateInterval, 0, 0, updateTimerCallBack, NULL); CFRunLoopAddTimer(CFRunLoopGetCurrent(), updateTimer, kCFRunLoopDefaultMode); CFRunLoopRun(); exit(0); }The accompanying elisp code will invoke that executable on a timer and change the theme based on the light reading.
(setq current-theme "dark") (defconst light-theme 'majapahit-light) (defconst dark-theme 'majapahit-dark) ;; will apply a dark theme if the room is dark, and a light theme if the room is ;; bright (defun change-theme-for-lighting () (let* ((current-light-sensor-reading (string-to-number (shell-command-to-string "./lmutracker")))) (if (< current-light-sensor-reading 100000) (when (not (string-equal current-theme "dark")) (load-theme dark-theme 1) (setq current-theme "dark")) (when (not (string-equal current-theme "light")) (load-theme light-theme 1) (setq current-theme "light"))))) ;; probably want to run this less frequently than every second (run-with-timer 0 1 #'change-theme-for-lighting)Edit 4/7/2019: Read a Russian translation of this post here.
-
Apr 2, 2018
Creating a new blog post in Emacs
Now that my blog is based on markdown text files, some new tooling options have opened!
- entire blog is under source control (done)
maketargets for common actions (e.g. create new post, deploy, serve dev version) (done)- git hooks for publishing (need to think about this more)
- blogging via emacs! (done!)
I just wrote this function to create a new posts file and open a buffer for editing it. In fact, it’s how I’m editing this post right now!
(defun new-blog-post () (interactive) (let ((post-title (read-string "Enter new post title: "))) (let* ((posts-dir "/ssh:vps:~/projects/blog/_posts/") (clean-title (replace-regexp-in-string "[^[:alpha:][:digit:]_-]" "" (s-replace " " "-" (downcase post-title)))) (new-post-filename (concat (format-time-string "%Y-%m-%d") "-" clean-title ".md")) (frontmatter-template "---\nlayout: post\ntitle: {title}\ndate: {date}\n---\n\n") (frontmatter (s-replace "{date}" (format-time-string "%Y-%m-%d %H:%m %z") (s-replace "{title}" post-title frontmatter-template))) (new-post-file (expand-file-name new-post-filename posts-dir))) (if (file-exists-p new-post-file) (message "A post with that name already exists.") (write-region frontmatter nil new-post-file) (find-file new-post-file)))))This was also the first elisp function I wrote :)
-
Mar 31, 2018
under construction
I was having some headaches with my existing shared hosting provider, so I decided to move this site to a VPS. I also didn’t want to run a LAMP stack, so I’ve moved this blog from WordPress to Jekyll. Please pardon the appearance as I find time to iron things out.